Conductive Hearing Loss
It is caused by damage to the outer or middle ear

Sound waves are blocked as they travel through the outer or middle ear. As sound cannot be transmitted efficiently, the sound energy reaching the inner ear is weak. Conductive hearing loss can be caused by infection, fluid in the middle ear, damage to the ossicles of the middle ear, perforation of the tympanic membrane, or the presence of a foreign body or sebum in the ear canal.
The main symptoms are:
Faint or dull perception of speech and other sounds
Ear pain or fluid discharge
Redness or swelling of the outer part of the ear
Pressure or feeling of fullness inside the ear
Sensorineural hearing loss
It is caused by damage to the inner ear
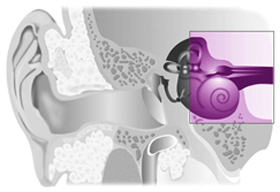
Sound waves travel normally through the outer and middle ear, while the inner ear is unable to pick up the vibrations or is unable to send the vibrations to the brain. It usually occurs in both ears. Sensorineural hearing loss can be caused by infection, disease, certain medications, excessive noise, problems from birth, and aging.
The main symptoms are:
Perception of speech and other sounds with distortion or lack of clarity
Difficulty hearing certain tones (usually high tones/frequencies)
Hearing a continuous or intermittent ringing or buzzing sound
Difficulty in understanding speech in the presence of noise
Mixed Hearing Loss
It is caused by damage to both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear

Typically, sound waves are not effectively transmitted to the inner ear, are not detected, and do not permeate to the brain. For this reason, mixed hearing loss is a combination of transmission and sensorineural hearing loss.
The main symptoms are:
Faint or dull perception of speech and other sounds
Ear pain or fluid discharge
Perception of speech and other sounds with distortion or lack of clarity
Difficulty understanding speech in the presence of noise
Central hearing loss
It is caused by damage to the auditory nerve or auditory centers in the brain.
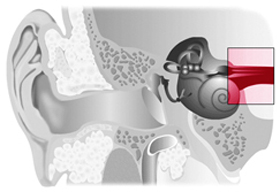
Sound waves are normally transmitted through all three parts of the ear, but either the auditory nerve is unable to transmit the electrical impulses to the brain, or the brain's auditory centers are not receiving the signals correctly. A central hearing loss can be caused by brain injuries, diseases or tumors.
The main symptoms are:
Perception of sounds without the possibility of understanding
